

Effects of alcohol on memory include disruption of various memory processes, affecting both formation and recall of information.
Alcohol acts as a general central nervous system depressant, but it also affects some specific areas of the brain to a greater extent than others. Memory impairment caused by alcohol has been linked to the disruption of hippocampal function—particularly affecting gamma-Aminobutyric acid (GABA) and N-methyl-D-aspartate (NMDA) neurotransmission which negatively impacts long-term potentiation (LTP).[1] The molecular basis of LTP is associated with learning and memory.[2] Particularly, damage to hippocampal CA1 cells adversely affects memory formation,[3] and this disruption has been linked to dose-dependent levels of alcohol consumption.[4] At higher doses, alcohol significantly inhibits neuronal activity in both the CA1 and CA3 pyramidal cell layers of the hippocampus.[5][6][7] This impairs memory encoding,[8] since the hippocampus plays an important role in the formations of new memories.

El alcohol también actúa como un modulador alostérico positivo de los receptores GABA , específicamente del tipo GABA A. [9] Tras la activación, estos receptores GABA conducen Cl- , lo que da como resultado una hiperpolarización neuronal . Esta hiperpolarización disminuye la posibilidad de que se produzca un potencial de acción y, por tanto, tiene un efecto inhibidor sobre la neurotransmisión en el sistema nervioso central . Los subtipos de receptores GABA A varían en su sensibilidad a la dosis de alcohol consumida. Además, la ingesta aguda de alcohol promueve la neurotransmisión GABAérgica a través de la liberación presináptica de GABA, la desfosforilación de los receptores GABA A (aumentando la sensibilidad al GABA) y la elevación de los esteroides neuroactivos GABAérgicos endógenos . [10] La proteína quinasa C (PKC) se ha implicado en la modulación diferencial de la respuesta del receptor GABA A al alcohol, con efectos que dependen de la isoenzima PKC . [11] Los efectos del alcohol también han implicado a la proteína quinasa A en afectar la función del receptor GABA A , como la promoción de la sensibilidad. [12] La mejora de la transmisión GABAérgica debido al consumo de alcohol también puede ser provocada por esteroides neuroactivos, como la alopregnanolona , que actúan como agonistas del receptor GABA A. [10] [13] Tanto el consumo crónico de alcohol como la dependencia del alcohol están correlacionados con la expresión, las propiedades y las funciones alteradas del receptor GABA A que pueden contribuir a la tolerancia al alcohol. [10] Todavía queda mucho por descubrir sobre los efectos específicos y variables del alcohol tanto en el receptor GABA A como en sus subtipos.
At higher doses, ethanol also affects NMDA receptors (NMDARs) by inhibiting the ion current induced by NMDA, a glutamate receptor agonist.[14] This inhibition of synaptic excitation by alcohol has been shown to be dose-dependent (up to a certain point, after which it did not differ by much).[15] Alcohol appears to produce this inhibition by using a site of the NMDAR that is accessible from the extracellular environment.[16] Therefore, this inhibition of an ion current usually produced by NMDAR activation leads to decreased LTP in hippocampal areas.[17] Alcohol negatively affects LTP to a greater degree in immature versus mature animals.[18] In adolescents, alcohol decreases the expression of both the NMDAR NR2A subunit in the hippocampus and the NR1 subunit in the prefrontal cortex.[19] Studies have also found that a decrease in phosphorylation of 2B subunit in the prefrontal cortex, the hippocampus, the nucleus accumbens, and the striatum.[20] NMDARS may be affected by PKA regulation due to the actions of alcohol.[21] Alcohol's effects on GABAA neurotransmission may indirectly inhibit the activity of the NMDAR, and they may contribute to its blockade of LTP induction; however, alcohol's direct effects on NMDAR alone are sufficient for the inhibition of LTP.[22] The varying dose-dependent response to alcohol relies on the combined interactions and responses of the GABAA receptors, NMDARs, and metabotropic glutamate receptors subtype 5 (mGluR5).[23][24][25] These changes prevent excitatory synaptic transmissions from occurring, affecting synaptic plasticity and, in turn, memory and learning. However, there is still much yet to be elucidated concerning specific molecular mechanisms of how alcohol affects memory formation.
Alcohol also impairs and alters the functioning in the cerebellum, which affects both motor function and coordination.[26] It has a notable inhibitory effect on the neurons of the cerebral cortex, affecting and altering thought processes, decreasing inhibition, and increasing the pain threshold. It also decreases sexual performance by depressing nerve centers in the hypothalamus.[27][28] Alcohol also has an effect on urine excretion via inhibition of anti-diuretic hormone (ADH) secretion of the pituitary gland. Lastly, it depresses breathing and heart rate by inhibiting neuronal functioning of the medulla.[29]
Long-term memory (LTM) has both a long duration and a large capacity.[30] Memories that are stored in LTM can last from a few days to a lifetime.[30] LTM consists of both explicit memory (requiring conscious awareness) and implicit memory (unconscious awareness).[30] Information selected for LTM goes through three processes. First of all, in the encoding stage, information from the senses is incorporated into mental activity in the form of a memory.[30] Secondly, storage involves taking this information and holding it indefinitely in memory.[30] Lastly, retrieval is the ability to recall information from the long-term memory storage. Each of these processes can be affected by alcohol.[30]

Explicit memory requires conscious and intentional effort for recall.[30] It includes both episodic memory (for specific events, such as a party) and semantic memory (for general information, such as one's name).[30]
Alcohol impairs episodic encoding, specifically for cued recall, recognition of completed word fragments, and free recall.[31] A blackout is an example of a difficulty in encoding episodic memories due to alcohol. Blackouts are caused by a rapid increase in blood alcohol concentration (BAC) which in turn distorts the neurons in the hippocampus.[32] This distortion impairs a person's ability to form new episodic memories.[32]
Las dosis altas de alcohol alteran gravemente el proceso de almacenamiento de las memorias semánticas. [33] Se ha descubierto que el alcohol perjudica el almacenamiento de estímulos nuevos, pero no el de la información previamente aprendida. [33] Dado que el alcohol afecta al sistema nervioso central , dificulta el funcionamiento del almacenamiento semántico al restringir la consolidación de la información a partir de la codificación. [33]
La recuperación de la memoria explícita se ve afectada significativamente por el alcohol. En comparación con los participantes sobrios, los participantes intoxicados tuvieron un desempeño bastante deficiente en una tarea de recuerdo de eventos cotidianos (es decir, memoria episódica). [34] Los participantes intoxicados también responden más lentamente en tareas de tiempo de reacción. [35] El alcohol también afecta negativamente a la recuperación en tareas de reconocimiento de palabras. [31] Cuando tanto la codificación como la recuperación tienen lugar durante la intoxicación, sorprendentemente hay más alteraciones en el recuerdo con señales que en el recuerdo libre. [31] En términos de diferencias de género en los procesos de recuperación, las mujeres tienden a obtener puntuaciones más bajas que los hombres en las tareas de recuerdo cuando están intoxicadas. [35]
La memoria implícita no requiere un esfuerzo consciente o intención para recordarla. [30] Ocurre cuando la experiencia previa influye en el desempeño en una determinada tarea. [30] Esto es evidente en los experimentos de preparación . La memoria implícita incluye la memoria procedimental , que influye en nuestros comportamientos cotidianos, como andar en bicicleta o atarse los zapatos. [30] Las personas pueden realizar estas habilidades sin siquiera pensar en ellas, lo que significa que la memoria procedimental funciona automáticamente. Si bien la recuperación de la memoria explícita se ve gravemente afectada por el alcohol, la recuperación de la memoria implícita no lo es. [34] Los sujetos intoxicados obtienen puntuaciones más altas en tareas de reconocimiento (que implican memoria implícita) que en tareas de recuerdo (que implican memoria explícita). [34]
La memoria a corto plazo se refiere al almacenamiento temporal de pequeñas cantidades de información en intervalos cortos. [30] La amplitud de dígitos se refiere a la cantidad propuesta de piezas de información (5-9) que se pueden almacenar en la memoria a corto plazo. Esto también se conoce como el número mágico siete, más o menos dos. Si se almacenan más piezas de información que esta, las nuevas reemplazarán a las anteriores. [36] Se ha descubierto que la intoxicación por alcohol tiene efectos disociativos tanto en la memoria a corto plazo como en el funcionamiento cognitivo. [37] [38]

Alcohol affects the functioning of the brain. Neurochemical changes occurring in the anterior cingulate are correlated with altered short-term memory functions in the brains of young alcoholic men.[39] fMRIs of alcohol-dependent women displayed significantly less blood oxygen in the frontal and parietal regions, especially in the right hemisphere.[40] This is supported by findings of short-term memory impairment by lesions of both the parietal lobe[41] and the prefrontal cortex.[42] Associations between third ventricle volume and cognitive performance on memory tests have been found in alcoholics.[43] Specifically, increases in third ventricular volume correlate with a decline in memory performance.[43]
Short-term memory is commonly tested with visual tasks. Short-term memory, especially for non-verbal and spatial material, are impaired by intoxication.[43] Alcohol decreases iconic memory (a type of visual short-term memory).[44] With BACs between 80 and 84 mg/dl, more intrusion errors occur in a delayed recall task compared to a control group.[45] Intrusion errors, which represent reflective cognitive functioning, occur when irrelevant information is produced. Alcoholics have less control of inhibiting intrusions.[45] Acute alcohol intoxication in social drinkers caused more intrusion errors in delayed recall tasks than in immediate free recall tasks.[45] Acute alcohol intoxication increases the susceptibility to interference, which allows for more intrusion errors when there is a short delay.[45] Free recall (given list of words then asked to recall list) is significantly lower and therefore impaired by alcohol intoxication.[46][47] Encoding deficits were found in verbal free recall and recognition tasks under the influence of alcohol.[48] A discrimination task found significant alcohol-related impairments both in depth perception and in visual short-term memory.[49] State-dependent learning and relearning studies in male heavy drinkers demonstrate that the condition of intoxication while learning and sobriety when tested caused a performance deficit in free recall tasks.[50] These findings are supportive of alcohol-induced storage deficits (not retrieval deficits).[50] The effects of acute alcohol consumption on visual short-term memory, stereoscopic depth perception, and attention were all studied. A 33% alcohol condition showed significant impairments both in depth perception and in visual short-term memory (assessed by the vernier discrimination task).[51]
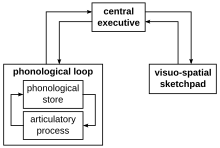
Working memory allows one to keep things in mind while simultaneously performing complex tasks.[30] It involves a system for both the temporary storage and the manipulation of information, subsequently forming a crucial link between perception and controlled action.[52] Evidence suggests that working memory involves three components: the central executive which controls attention, the visuo-spatial sketchpad which holds and manipulates spatial information, and the phonological loop which performs a similar function for auditory and speech-based information.[52]
El consumo de alcohol tiene efectos sustanciales y mensurables en la memoria de trabajo, aunque estos efectos varían mucho entre las respuestas individuales. No se sabe mucho realmente sobre los mecanismos neuronales que subyacen a estas diferencias individuales. [53] También se ha descubierto que el alcohol perjudica la memoria de trabajo al afectar las estrategias mnemotécnicas y los procesos ejecutivos en lugar de reducir la capacidad básica de retención de la memoria de trabajo. Los niveles aislados de intoxicación alcohólica aguda-moderada no alteran físicamente las estructuras que son críticas para el funcionamiento de la memoria de trabajo, como la corteza frontal , la corteza parietal , la corteza cingulada anterior y partes de los ganglios basales . [37] Un hallazgo sobre los efectos del alcohol en la memoria de trabajo señala que el alcohol reduce la memoria de trabajo solo en individuos con una alta capacidad de memoria de trabajo de base, [54] lo que sugiere que el alcohol podría no afectar uniformemente a la memoria de trabajo en muchos individuos diferentes. El alcohol parece perjudicar la capacidad de la memoria de trabajo para modular la inhibición de la respuesta. [54] El alcohol desinhibe el comportamiento, pero solo lo hace en individuos con una baja capacidad de memoria de trabajo de base. [54] Un hallazgo interesante es que el incentivo para desempeñarse bien con tareas de medición de la memoria de trabajo bajo la influencia del alcohol , de hecho , tiene algún efecto sobre la memoria de trabajo, ya que aumenta las puntuaciones en la tasa de escaneo mental y el tiempo de reacción al estímulo; sin embargo, no redujo el número de errores en comparación con los sujetos sin incentivo para desempeñarse bien. [55] Incluso la intoxicación alcohólica aguda (una concentración de alcohol en sangre de 0,08-0,09%) produce un deterioro sustancial de los procesos de memoria de trabajo que requieren estrategias de ensayo mnemotécnico. [37] Es menos probable que el alcohol dañe una tarea de memoria de trabajo que no se basa en el ensayo de memoria o estrategias mnemotécnicas asociadas. [37] Debido a esto, la memoria de trabajo es muy susceptible a fallar cuando un individuo participa en tareas que involucran retención relacionada con secuencias auditivas y visuales. [37]
An interesting example of this is the failure of guitarists or other musicians performing concerts to cue in on auditory patterns and make it known that their performance is hindered by intoxication, whereas professional basketball (a less sequence-heavy activity for working memory) standout Ron Artest admitted in an interview with Sporting News to drinking heavily during half-time early in his career and the fact that it had little—if not any recognizable—effect on his working memory. His former coach Fran Fraschilla has gone on record saying:[56]
It's a surprise because every day at practice, he came out in a mood to play. He came out in a basketball rage. He was fully committed; he wanted to let our upperclassmen know that he was the alpha male. It never came up that he had any sort of a problem with alcohol. This is the first I've heard of it.
Alcohol has been shown to have just some long-term effects on working memory. Findings have shown that in order for working memory to be substantially affected, long-term heavy drinking must be sustained over a long period of time, as up to one drink per day does not impair any cognitive function and may actually decrease the risk of a cognitive decline.[57] Furthermore, chronic alcoholism is associated with the impairment in both sustained attention and visual working memory. As a result, alcoholics have reduced ability, but not necessarily inability, to perform these executive tasks. This is assumed to be subserved by regions of the prefrontal cortex.[58] While it may not serve as a surprise that chronic alcoholism is linked to any decreased cognitive function such as working memory, one surprising finding is not only that even moderate levels of alcohol consumption during pregnancy were shown to have an adverse effect on the child's working memory when tested at 7.5 years of age, but also that working memory may be the most important aspect of attention that is adversely affected by prenatal alcohol exposure.[59]
Prospective memory involves remembering to carry out an intended action in the future without an explicit reminder.[30] Alcohol has been found to impair this ability. Chronic heavy alcohol users report significantly more prospective forgetting compared to low-dose and alcohol-free controls.[60] The Prospective Memory Questionnaire assesses short-term habitual prospective memory, long-term episodic prospective memory, and internally cued prospective memory.[60] Chronic heavy alcohol users reported significantly greater deficits for all three aspects of prospective memory.[60] Individuals that report heavy alcohol use report 24% more difficulties with prospective memory than those who report that they are light drinkers and 30% more difficulties than those who report that they never drink.[61] The effects of alcohol on prospective memory can also be assessed in the laboratory by simulating prospective memory tasks that individuals face in everyday life. Individuals who are given 0.6 g/kg alcohol prior to performing prospective memory tasks do significantly poorer than a placebo group.[62] Alcohol can damage the prefrontal and frontal areas of the brain, and this may be responsible for prospective memory impairments since prospective memory performance is highly correlated with frontal executive functions.[60]
The memory inhibiting effects of alcohol are often a prominent topic in popular culture. It appears in movies, books, and television shows. Several movies show characters drinking alcohol to the point of memory loss and awakening the next morning with a host of problems due to actions they performed while intoxicated.
One example is The Hangover, where three groomsmen lose the groom during a bachelor party in Las Vegas, so they retrace their steps to find him.[63] The characters still had functioning implicit/procedural memory, which allowed them to carry out the many acts they performed that night, but their episodic memory was impaired and thus they had no recollection of the events occurring. In addition to alcohol the characters were also under the influence of flunitrazepam.
Another movie is What Happens in Vegas. After an intoxicated night in "Sin City," two people wake-up to find they got married.[64]
Songs such as Waking Up in Vegas by Katy Perry[65] and Last Name by Carrie Underwood[66] also depict characters waking up and not remembering the night before due to alcohol consumption.
By some accounts, popular culture makes light of the memory problems that can result from alcohol consumption.
The court case R. v. Daviault [1994] concerned the viability of a legal defense based on intoxication.