A symmetric relation is a type of binary relation. Formally, a binary relation R over a set X is symmetric if:[1]
where the notation aRb means that (a, b) ∈ R.
An example is the relation "is equal to", because if a = b is true then b = a is also true. If RT represents the converse of R, then R is symmetric if and only if R = RT.[2]
Symmetry, along with reflexivity and transitivity, are the three defining properties of an equivalence relation.[1]
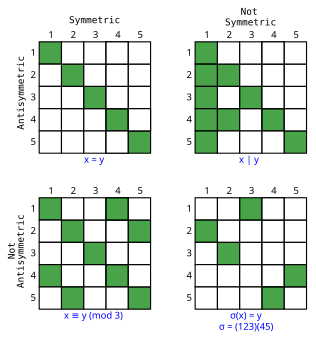
By definition, a nonempty relation cannot be both symmetric and asymmetric (where if a is related to b, then b cannot be related to a (in the same way)). However, a relation can be neither symmetric nor asymmetric, which is the case for "is less than or equal to" and "preys on").
Symmetric and antisymmetric (where the only way a can be related to b and b be related to a is if a = b) are actually independent of each other, as these examples show.
Note that S(n, k) refers to Stirling numbers of the second kind.